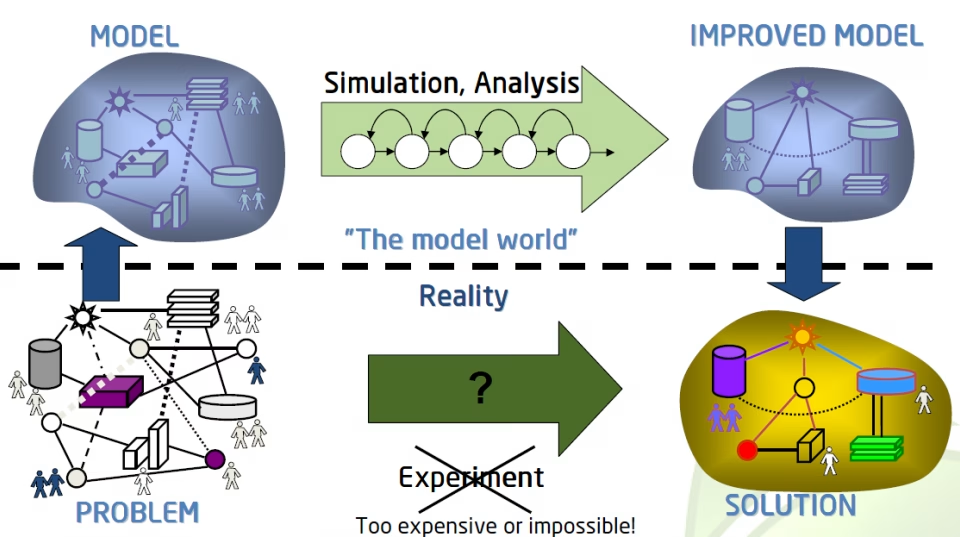
10 Reasons to Implement Modelling and Simulations Into Your Drug Development Program
Case Study: Translating Non-Clinical Models Into Human PK and Efficacy Predictions
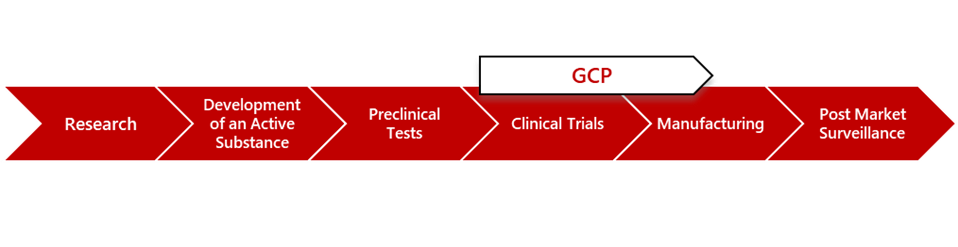
Latest ICH GCP E6(R3) Amendment Explained
The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) has unveiled a transformative update to its Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines with the final version release of ICH E6(R3) in January 2025. This revision modernises clinical trial standards to align with technological advancements, ethical complexities, and evolving scientific methodologies. Let’s break down what this means for researchers, sponsors, and ethics committees—and why it matters.
Why E6(R3)?
The 2016 ICH E6(R2) guideline laid the groundwork for ethical and reliable clinical trials but lacked provisions for today’s digital-first, decentralised trials. E6(R3) addresses gaps by integrating cutting-edge technology, enhancing participant protections, and fostering a culture of proactive quality management.
6 Key Changes in E6(R3)
1. Modular Structure for Flexibility
- Old (R2): Linear sections focused on principles, roles, and processes.
- New (R3): A modular framework with:
- Core Principles (e.g., robust science, transparency).
- Annexes detailing roles for IRBs, investigators, sponsors, and data governance.
- Appendices covering protocols, essential records, and investigator brochures.
This structure adapts to diverse trial types, from traditional studies to decentralised, tech-driven designs.
2. Principles with Purpose
E6(R3) expands from 13 to 18 principles, emphasising:
- Quality by Design: Build quality into trials from the start.
- Risk Management: Prioritise risks to participant safety and data reliability.
- Transparency: Mandate trial registration and public sharing of results.
- Technology Integration: Use digital tools ethically and efficiently.
3. Tech-Driven Trials
The guidelines embrace modern tools to streamline trials:
- Digital Consent: eConsent via video, electronic signatures, or telephonic approvals (learn more about eConsent best practices).
- Wearables & Sensors: Integrate real-time data from devices (e.g., heart rate monitors).
- Data Governance: Ensure traceability with metadata and audit trails (see ICH E6(R3) draft).
- Source Records: Replace paper-based “source documents” with digital records (e.g., EHRs, ePROs).
4. Stronger Ethical Safeguards
- Emergency Research: Clear protocols for consent in urgent settings (read Bhatt 2020 on COVID-19 challenges).
- Participant Privacy: Protect data from wearables, apps, and social media.
- Inclusivity: Require assent for minors and vulnerable groups.
- Re-Consent: Update participants on protocol changes affecting risks.
5. Quality Over Compliance
- Proactive Quality Systems: Move beyond reactive checks to embed quality in trial design (see ICH E8(R1)).
- Risk-Proportionate Monitoring: Reduce on-site visits for low-risk trials.
- Root-Cause Analysis: Investigate noncompliance systematically.
6. Expanded Responsibilities
- IRBs/IECs: Review digital tools, ensure privacy, and oversee safety reporting (e.g., SUSARs).
- Investigators: Manage delegated tasks (e.g., third-party vendors) and secure digital data.
- Sponsors: Validate computerized systems, implement risk-based monitoring, and ensure data integrity.
Implementation Challenges
While E6(R3) aims for global harmonization, adoption faces hurdles in regions like India, where local guidelines (e.g., NDCTR 2019) lag behind. Key gaps include:
- No provisions for risk-based monitoring or computerized systems.
- Outdated ethical frameworks for digital trials.
- Urgent need for training on eConsent, decentralized trials, and data governance.
The Road Ahead
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed weaknesses in traditional trial conduct, from inconsistent data collection to ethical dilemmas in emergency research. E6(R3) addresses these gaps by:
- Encouraging decentralised trials to improve participant access (explore Decentralized Trial Strategies).
- Leveraging AI and big data for smarter trial design.
- Prioritising participant-centricity through transparency and inclusivity.
For stakeholders, the message is clear: Adapt or risk noncompliance. Training programs focused on digital tools, ethics, and risk management will be critical to success.
Further Reading & Resources
- ICH Official Website
- FDA Guidance on GCP
- EMA Clinical Trials Regulation
- Ethical Implications of Pandemic Trials (Jedlickova 2021)
Final Thoughts
ICH E6(R3) isn’t just an update—it’s a paradigm shift. By embracing technology, ethics, and quality, it sets a new standard for clinical trials in the 21st century. As the draft moves toward finalization, researchers and regulators must collaborate to ensure these guidelines translate into safer, more reliable, and inclusive trials worldwide.
Stay informed, stay compliant, and let’s shape the future of clinical research together.